The field of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping has witnessed a significant transformation with the introduction of next-generation aerial tools such as Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers. These advanced technologies have revolutionized the way aerial surveying is conducted, offering a range of benefits that enhance georeferencing accuracy, streamline flight path planning, and improve remote sensing data collection.
How is GNSS Transforming Aerial Surveying?
GNSS receivers are playing a pivotal role in transforming aerial surveying practices by enhancing georeferencing accuracy. These tools provide precise positioning data, enabling surveyors to map locations with unparalleled precision. –
Streamlining Flight Path Planning
One significant advantage of utilizing such receivers in aerial surveying is the streamlined flight path planning process. These tools enable surveyors to optimize flight routes, ensuring efficient data capture and coverage of the area of interest. By automating flight path planning, they contribute to smoother survey operations.
What Advantages Do Next-Gen Aerial Tools Offer Over Traditional Methods?
Next-gen aerial tools offer several advantages over traditional methods of GIS mapping. One key benefit is enhanced data resolution, allowing for detailed and accurate mapping of geographic features.
Furthermore, these tools provide real-time data processing capabilities, enabling surveyors to analyze and interpret data on-site, leading to improved decision-making and actionable insights.
Increased Efficiency in Mapping Large Areas
Another advantage of next-gen aerial tools is the increased efficiency in mapping large areas. By leveraging IMU and GNSS technology, surveyors can cover expansive regions in a shorter time frame, reducing overall project timelines and costs. This efficiency facilitates the mapping of vast territories with precision and speed.
Challenges Faced in Adopting Next-Gen Aerial Tools for GIS Mapping
Despite their numerous benefits, the adoption of next-gen aerial tools in GIS mapping poses certain challenges. Cost considerations are a significant factor, as investing in state-of-the-art equipment and training personnel can be financially demanding. Additionally, interoperability issues with existing systems may arise, requiring seamless integration to ensure compatibility and data consistency.
Training and Skill Requirements for Operation
Another challenge faced in adopting next-gen aerial tools is the need for specialized training and skill development among users. Operating IMU GNSS receivers requires technical expertise, necessitating ongoing training programs to ensure proficiency and competence in utilizing these advanced technologies effectively.
Future Trends and Innovations in Aerial Surveying Technologies
The future of aerial surveying technologies is poised for exciting developments and innovations. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in data analysis is one such trend, offering advanced algorithms for processing and interpreting aerial data efficiently.
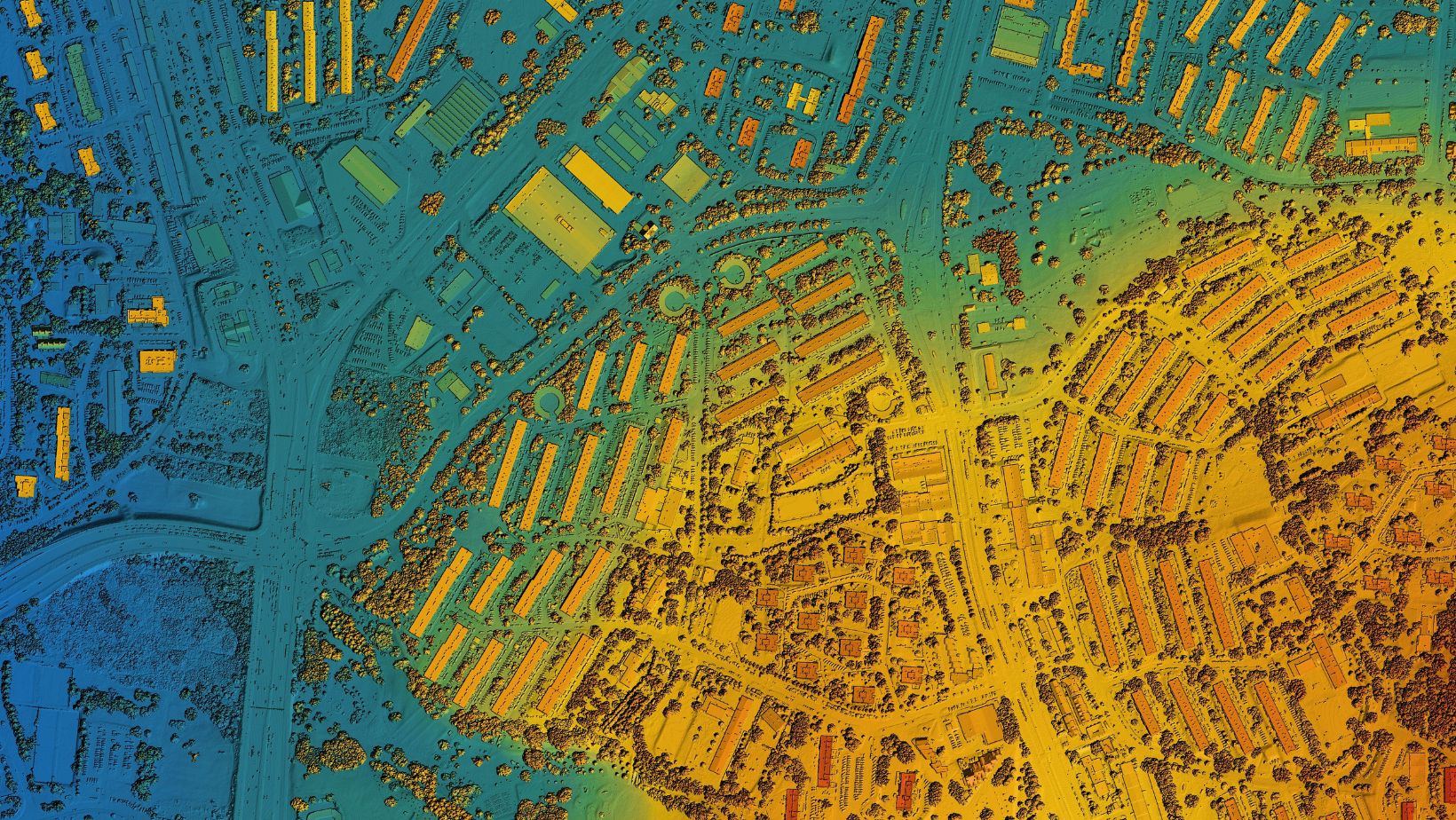
Moreover, advancements in LiDAR technology for 3D mapping are enhancing the capabilities of next-gen aerial tools, enabling high-resolution mapping and modeling of terrain and structures.
Enhanced Collaboration through Cloud-Based GIS Platforms
Cloud-based GIS platforms are revolutionizing collaboration and data sharing in aerial surveying projects. By providing a centralized and accessible data repository, these platforms facilitate seamless collaboration among stakeholders and enable real-time updates and analysis. The integration of cloud technologies enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of GIS mapping initiatives.












